Hack 67. Manage Word Documents from Access
Tap into the Word object library to copy Access data directly into a Word document. As is the case with all Microsoft Office products, Word has a significant number of exposed objects and methods to work with, and becoming familiar with a decent number of these is a challenge worth undertaking. This hack creates a procedure that places data from Access into a table in a Word document. The concepts here also apply to other Word manipulations. Perhaps this will be your springboard into a new avenue of Office development. 7.10.1. Hooking into WordIn an Access code module, we're going to place a routine to work with an existing Word document. To make this a little easier, we'll set a reference to Word's object library. We'll do this inside the Access VB Editor, using the Tools Figure 7-42. Setting a reference to the Word object library
7.10.2. The CodeThe next thing to do is enter the code. This must go into an Access code module:
Sub Access_to_Word()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Set conn = CurrentProject.Connection
Dim recset As ADODB.Recordset
Set recset = New ADODB.Recordset
Dim row_num As Integer
Dim col_num As Integer
Dim word_doc As Object
'Assumes Word doc is in same path - change name and path as needed
Set word_doc = GetObject(Application.CurrentProject.Path & "\Customers.doc")
'get data from Access table
recset.Open "Select * From Customers Where State='OR'", _
conn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic
'get the record count - used to create Word Table
recset.MoveLast
recset.MoveFirst
With word_doc
'navigate to Word bookmark and create table
'the number of table rows matches the recordset row count
'the number of table columns matches the number of recordset fields
.Bookmarks("Customers").Select
.Tables.Add Range:=Selection.Range, _
NumRows:=recset.RecordCount, NumColumns:=recset.Fields.Count
For row_num = 1 To recset.RecordCount
For col_num = 1 To recset.Fields.Count
.Tables(.Tables.Count).Cell(row_num, col_num).
Select Selection.TypeText recset.Fields(col_num - 1)
Next col_num
'next database record
recset.MoveNext
Next row_num
End With
recset.Close
Set recset = Nothing
Set word_doc = Nothing
MsgBox "done"
End Sub
Here are some highlights of this code:
7.10.3. The Data Has Landed IntactAfter running this code, the document has a table with the data, as shown in Figure 7-43. Note that there is no connection back to Access; the data is just essentially part of the Word document. Note that this simplistic example assumes a number of things: the bookmark exists, there is no existing table, and the Access table isn't too large in terms of rows and fields to make the Word table too densely packed. Nonetheless, this hack serves as a brief introduction to tapping into Word objects. Because the reference has been set to the library, you can now use the Object Browser in Access to review Word's objects. Figure 7-43. The Access data in a Word table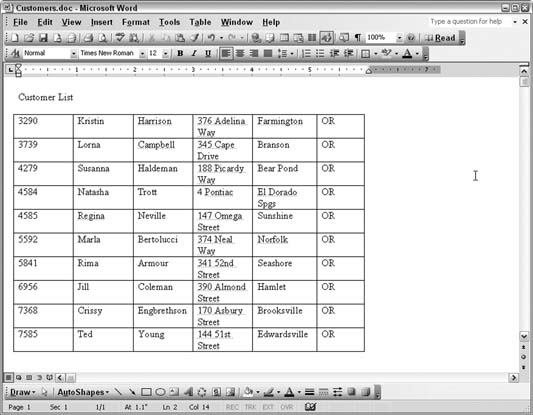
|