Template Method
Intent
Define the skeleton of an algorithm in an operation, deferring some
steps to client subclasses. Template Method lets subclasses redefine
certain steps of an algorithm without changing the algorithm's
structure.
Problem
Two different components have significant similarities, but demonstrate
no reuse of common interface or implementation. If a change common to
both components becomes necessary, duplicate effort must be expended.
Discussion
The component designer decides which steps of an algorithm are
invariant (or standard), and which are variant (or customizable). The
invariant steps are implemented in an abstract base class, while the
variant steps are either given a default implementation, or no
implementation at all. The variant steps represent "hooks", or
"placeholders", that can, or must, be supplied by the component's
client in a concrete derived class.
The component designer mandates the required steps of an algorithm, and
the ordering of the steps, but allows the component client to extend
or replace some number of these steps.
Template Method is used prominently in frameworks. Each framework
implements the invariant pieces of a domain's architecture, and defines
"placeholders" for all necessary or interesting client customization
options. In so doing, the framework becomes the "center of the
universe", and the client customizations are simply "the third rock
from the sun". This inverted control structure has been affectionately
labelled "the Hollywood principle" - "don't call us, we'll call you".
Structure
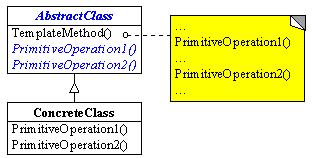
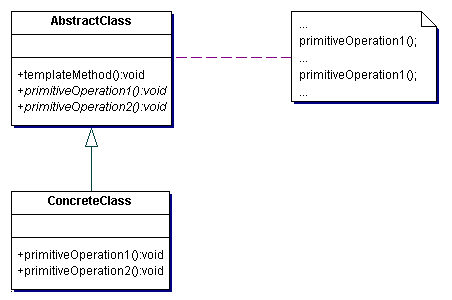
Example
The Template Method defines a skeleton of an algorithm in an operation,
and defers some steps to subclasses. Home builders use the Template
Method when developing a new subdivision. A typical subdivision
consists of a limited number of floor plans with different variations
available for each. Within a floor plan, the foundation, framing,
plumbing, and wiring will be identical for each house. Variation is
introduced in the later stages of construction to produce a wider
variety of models. [Michael Duell, "Non-software examples of software
design patterns", Object Magazine, Jul 97, p54]
Non-software example
Rules of thumb
Strategy is like Template Method except in its granularity. [Coplien,
C++ Report, Mar 96, p88]
Template Method uses inheritance to vary part of an algorithm. Strategy
uses delegation to vary the entire algorithm. [GOF, p330]
C++ Demos | Java Demos | Lab


